Subscribe for email alerts
Donate to Science & Enterprise
|
By Alan, on February 22nd, 2022  (Pete Linforth, Pixabay. https://pixabay.com/illustrations/dna-life-biotechnology-evolution-4068826/) 22 Feb. 2022. Food and Drug Administration approved 17 new medications in 2021 addressing genetic targets, according to data from a precision medicine advocacy group. The annual report of the Personalized Medicine Coalition in Washington, D.C. indicates both the number and percentage of new precision treatments approved by FDA in 2021 are similar but down slightly from 2020.
Precision or personalized medicines are prescribed by physicians to meet a patient’s molecular make-up, based on results of diagnostics, and the individual’s medical history. The Personalized Medicine Coalition’s annual report says FDA approved 17 new drugs and biologics meeting this definition in 2021, making up 35 percent of all new therapies last year. In 2020, FDA approved 20 new precision drugs and biologics, comprising 39 percent of all new treatments. Since 2015, precision medications account for 25 to 42 percent of all new drugs or biologics approved each year by FDA.
Seven of the 17 new precision drugs and biologics approved by FDA are cancer therapies, mainly for treating non-small cell lung cancer, but also bile duct and uterine cancer, and chronic myeloid leukemia. Each of these therapies addresses specific biomarkers, molecular indicators revealed through genetic testing. In addition, the report notes approval of two cell therapies approved by FDA last year to treat blood related cancers, large B-cell lymphoma and multiple myeloma. In both cases, patients’ T-cells are genetically altered, then re-infused as therapeutics.
New or expanded precision medicine diagnostics
FDA approved another seven new precision drugs or biologics to treat rare or inherited diseases indicated by specific biomarkers, according to the report. The approved medications treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Pompe disease, Von Hippel-Lindrau disease, progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis, myasthenia gravis, heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, and molybdenum cofactor deficiency. Three other approved precision therapies address HIV, and severe cases of itching (pruritis) and blood-vessel inflammation (vasculitis).
The PMC report points out related FDA actions in 2021 authorizing diagnostic tests for precision therapies. The group says the agency cleared or broadened the scope of nine companion diagnostics for precision drugs. The report also highlights recognition for the Oncology Knowledge Base at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, as one of FDA’s human genetic variant databases that document evidence of links between genetic variations and diseases or conditions.
PMC president Edward Abrahams says in an organization statement the findings show “personalized medicines have accounted for more than a quarter of newly approved drugs for each of the last seven years and for more than a third of the drugs approved since 2017, not to mention the approval of new or expanded indications for a countless number of paradigm-shifting diagnostic tests,” adding that the report “leaves no question that the era of personalized medicine is upon us, presenting both opportunities and challenges for patients and health systems.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on February 21st, 2022  International Space Station (NASA.gov) 21 Feb. 2022. Several experiments from companies and academic labs arrived today at the International Space Station to test effects of microgravity and other conditions. NASA announced in a statement this morning that astronauts on the ISS retrieved the space craft with the experiments launched on Saturday from the agency’s flight facility at Wallops Island, Virginia.
The space cargo includes two health-related experiments from industry labs. Biotechnology company MicroQuin in Cambridge, Massachusetts is testing effects of weightless conditions on breast and prostate cancer cell development. The tests aim to compare cancer cell growth and maturation to healthy cells in microgravity that better simulates internal conditions in the body. “When you send cells into space, in particular cancer cells,” says MicroQuin president Scott Robinson in an ISS National Lab statement, “the signaling inside the cells changes considerably. These changes occur quite fast, and we don’t really understand exactly what those changes are and what causes them.”
The four year-old company is funding the project with a grant from Technology in Space Prize awarded by Center for the Advancement of Science in Space or Casis that operates the ISS National Lab. MicroQuin is a graduate of the MassChallenge technology incubator that partners with Casis and Boeing Company on the Technology in Space Prize.
Bubbles in microgravity
In another experiment, consumer products giant Colgate-Palmolive is testing effects of microgravity on live skin tissue samples. Astronauts already report evidence of rashes and irritation in space, as well as skin thinning after return to earth. The samples represent human skin tissue frozen at various points in time, to measure molecular and physiological responses to weightlessness as skin ages in space. Upon return of the samples to earth, researchers will conduct genetic and other analyses to identify biomarkers, or molecular indicators, that change in space, compared to similar samples on earth.
A team from University of Notre Dame in South Bend, Indiana is testing microgravity effects on bubbles forming on heated nanoscale structured metals. Because gravity influences formation of bubbles on Earth, weightless conditions are expected to reveal different fluid dynamics affecting surface tension and capillary forces on bubbles formed in space. Thermal bubbles, say the researchers, are useful for studying biomarkers in blood in low concentrations.
Tengfei Luo, aerospace and engineering professor at Notre Dame is leading the project. “When gravity-driven buoyancy is removed,” says Luo in an ISS National Lab statement, “we can more clearly study how the surface tension and capillary forces compete with each other.” Luo adds, “In a laboratory sample, the longer a bubble stays intact and the larger it grows, the more potential biomarkers it can collect.”
NASA says the space cargo includes a number of its own tests and experiments. The agency is testing effects of microgravity on glass optics, with an algorithm-driven module to prepare for glass fiber manufacturing in space. Another module is testing plant growth with hydroponic and aeroponic techniques to remove the need for soil, from seed germination through maturity. In a separate test, a solid-state lithium ion battery is being demonstrated on the ISS, made with inorganic and flame-retardant materials. Conventional lithium-ion batteries are made with liquids that can leak and catch fire.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on February 19th, 2022 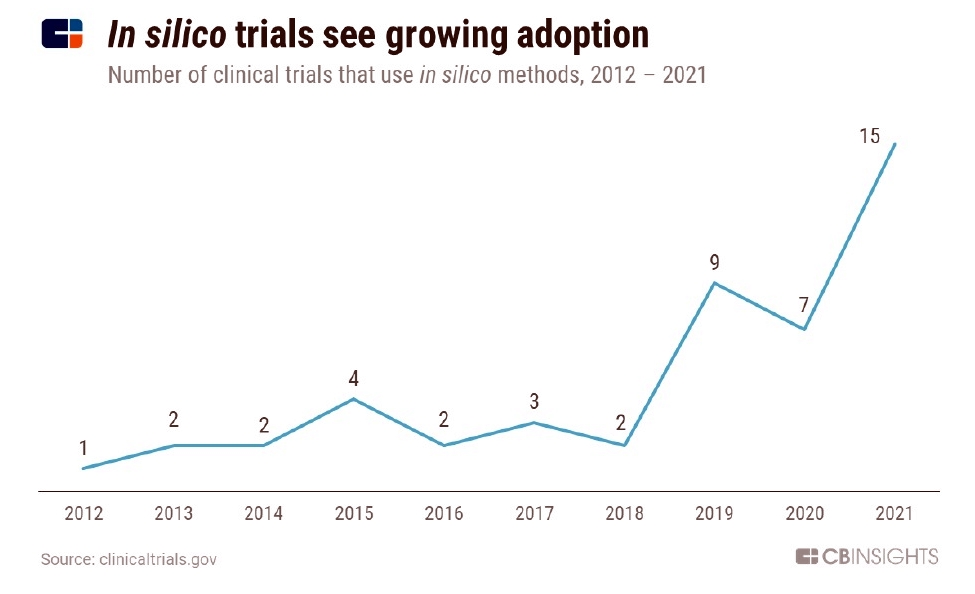 Click on image for full-size view (CB Insights) 19 Feb. 2022. A continuing topic covered in Science & Enterprise is innovations in clinical trials that test new drugs or medical devices with human subjects. The time and expense of clinical trials make up a sizable part of the overall costs of developing new treatments, which seem to be constantly growing.
The technology market intelligence company CB Insights highlighted the growing use of simulated clinical trials in its recent Tech Trends for 2022 report (registration required). The report notes that in 2021, 15 simulated or in silico trials, as they’re called, were underway, a rapid jump in this technique from the two trials reported 2018. CB Insights used data from ClinicalTrials.gov, the U.S. government’s clinical trials database, for the chart.
In silico trials, says CB Insights, are used today to supplement rather than replace, conventional clinical studies. Companies are using modeling and simulation to get a preview of likely outcomes of conventional trials, to help decide if a trial should proceed. Computational techniques are also used to add more diverse populations to studies that may be difficult to recruit, simulate placebo groups in studies where life-saving medications would otherwise be denied to trial participants, or test alternative treatment conditions.
CB Insights says the technology is still in its early stages, but the growing numbers and increasing market presence suggest more adoption in the near future. In silico trials will likely be a tool used as well with real-world evidence and algorithms to supplement conventional trial evidence, with the Food and Drug Administration becoming an active user of these data.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on February 18th, 2022  (National Institute of General Medical Sciences, NIH) 18 Feb. 2022. Light-activated stimulation of a precise set of nerve cells in the brainstem is shown to improve motor abilities in lab mice induced with Parkinson’s disease. A neuroscience team from University of Copenhagen in Denmark describe their techniques in the 26 Jan. issue of the journal Nature Communications.
Parkinson’s disease occurs when the brain produces less of the amino acid dopamine, a neurotransmitter that sends signals from one neuron or nerve cell to another. As the level of dopamine lowers, people with Parkinson’s disease become less able to control their bodily movements and emotions. Tremors associated with Parkinson’s disease can be treated with deep-brain stimulation, where an implanted device surgically sends electrical signals into affected brain regions, but the technique does not improve basic motor abilities like walking.
Copenhagen neuroscientist Ole Kiehn investigates nerve cell circuits affecting motor activity in the body. Among the lab’s research are studies of neuronal circuits connecting the brainstem, the lower stalk-like part of the brain, with the spinal cord, particularly when dysfunctions in those circuits result in movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease. Kiehn and postdoctoral researcher Debora Masini, the paper’s first author, note that in people with Parkinson’s disease, reductions in dopamine affect neuron circuits in the basal ganglia, a region in the brain responsible for motor control.
The authors indicate another part of the brain called the pedunculopontine nucleus or PPN, located in the brainstem, also has neurons emitting signals affecting motor activity, but it first depends on signals from the basal ganglia. Masini and Kiehn hypothesize that using deep brain stimulation to activate certain responsive neurons, found in the caudal or tail-like area of the PPN, could overcome the loss of locomotion signals from the basal ganglia when dopamine is reduced.
Viruses expressing light-emitting proteins
The researchers induced Parkinson’s-like symptoms in a set of lab mice by chemically blocking dopamine production, which caused the animals to slow or stop motor activity. Tests show by blocking dopamine production, the mice emitted fewer motor activity signals from their basal ganglia to PPN neurons. Masini and Kiehn delivered stimulation to neurons in the PPN caudal area, using adeno-associated viruses, genetically altered benign viruses often used for gene therapy. In this case, the viruses expressed optogenetic or light-emitting proteins to stimulate the target neurons.
The authors say mice receiving the light-activated stimulation to the PPN exhibit normal leg movements. “When we stimulated these specific neurons in the caudal area of the PPN,” says Masini in a university statement, “the animals were able to walk normally, across longer distances and with normal walking speed, as opposed to before the stimulation, where they would display symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.”
Masini adds, “We systematically compared stimulation of different locations and cell types in a series of complementary experiments. And they all pointed towards the same conclusion. It strongly indicates these excitatory neurons in the caudal PPN are an ideal target for recovery of movement loss.”
Kiehn notes that advancing these techniques to clinical trials with electronic deep brain stimulation should proceed cautiously, since only caudal PPN neurons can be safely targeted. “It is a very delicate area,” says Kiehn, “because if we were to stimulate excitatory neurons in other areas than the caudal PPN, it would cause complete immobilization instead.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on February 17th, 2022  (Skeeze, Pixabay) 17 Feb. 2022. An analysis of genetic database records indicates a class of neurological diseases can be detected by sequencing of a person’s entire genome. Results of a study by researchers from Queen Mary University of London, genomic systems company Illumina, University College London, and Genomics England appear in today’s issue of the journal The Lancet Neurology.
A team led by neuroscientist Arianna Tucci with Queen Mary University and Genomics England, and vice-president for scientific research at Illumina Ryan Taft, seeks to find accessible and reliable methods for detecting repeat expansion disorders. These conditions result from expansions of simple sequence repeats, where base pairs of amino acids in DNA are repeated several times in tandem. More than 40 inherited or genetic diseases mainly affecting the nervous system are linked to repeat expansion, including Huntington’s disease, Friedreich ataxia, and fragile X syndrome. The authors cite data indicating repeat expansion disorders affect about 1 in 3,000 individuals.
One method for diagnosing inherited diseases is genomic sequencing that analyzes the order of base pairs making up DNA to identify disease-causing variations. In most cases, however, diagnostic genomic sequencing looks for a particular variant in DNA. Detecting an entire class of genetic disorders would require conducting many of these tests, a highly inefficient and expensive process.
In this study, researchers investigated the feasibility of whole genome sequencing to detect repeat expansion disorders. Whole genome sequencing is made possible by advances in sequencing technology that enables faster throughput and analytics to parse and reassemble the entire genome at a reasonable cost. Illumina in San Diego, a partner in the study, is a developer of genomic analysis systems, including whole genome sequencing.
Whole genome sequencing compared to PCR tests
The team analyzed genomic sequencing data stored in the 100,000 Genomes Project undertaken by Genomics England, a genetics research initiative funded by U.K.’s National Health Service and others. The project sequenced 100,000 genomes of some 85,000 U.K. residents with cancer or rare diseases through 2018, with data now made available for researchers. In this case, the study team looked for people with indicators of repeat expansion in samples from the 100,000 genomes database, and then compared the analysis to standard polymerase chain reaction or PCR diagnostics for neurological disorders in linked NHS medical records for identified individuals.
The team first analyzed the genomes of 404 persons with neurological disorders, identified by PCR diagnostics in their medical records. The results show whole genome sequencing identified 215 of 221 repeat expansion variations that match PCR diagnostics, with a true-positive sensitivity of 97 percent. Whole genome sequencing also correctly identified 1,316 of 1,321 non-repeated variations, with a true-negative specificity of 99 percent.
Researchers then sampled whole genomes of 11,631 participants in the 100,000 Genomes project. The data identified 81 cases of repeat expansions from the genomic records, and later confirmed as disease-related in 68 of those cases with PCR analytics. Of the remaining repeat expansions, 11 cases were not disease-related and two cases were found not to be expansions.
The authors conclude that implementing whole genome sequencing is a feasible diagnostic tool in cases where repeat expansion disorders are suspected. “This study demonstrates,” says Taft in a Genomics England statement, “that whole genome sequencing can be used in clinical laboratories for the diagnosis of patients who have a neurological disorder, such as Huntington’s disease. For the large percentage of patients with suspected repeat expansion disorders who remain undiagnosed, this should bring hope that a diagnosis may soon be possible.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on February 16th, 2022  (commonfund.nih.gov) 16 Feb. 2022. A start-up enterprise is developing a treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or ALS, spun off from university research labs and an ALS advocacy group. The new company, ProJenX in New York, is raising $5.1 million in seed funds to advance work begun by neuroscience researchers at Columbia University and the organization Project ALS.
ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder where neurons or nerve cells controlling muscles in the body begin to waste away, and can no longer send or receive signals from the brain or spinal cord. As the nerve cells stop functioning, muscles in the limbs, and later speech and breathing muscles, begin weakening and eventually stop functioning. Most people with the disease die of respiratory failure. According to Johns Hopkins University, ALS affects some 30,000 people in the U.S., with 5,000 new cases reported each year.
ProJenX seeks to advance a treatment candidate for ALS called prosetin into clinical trials. Prosetin is an optimized small-molecule compound discovered by researchers from Columbia University’s Project ALS Therapeutics Core, a joint initiative with Project ALS that advocates and raises money for research on ALS. In a paper published in Oct. 2019, researchers from Columbia and Project ALS identified prosetin as a synthesized compound that blocks actions of damaging enzymes known as mitogen-activated protein or MAP4 kinases. By blocking MAP4 kinases, prosetin reverses endoplasmic reticulum stress, pressure exerted on cells causing misfolded proteins, which in nerve cells can build-up and become toxic.
Granted orphan drug status
The Columbia/Project ALS team tested prosetin in lab mice, and found the compound penetrates the blood-brain barrier to block MAP4 kinases and protect nerve cells. In Aug. 2020, Food and Drug Administration designated prosetin as an orphan drug, which provides for extended market exclusivity, tax credits for clinical trials, and waiver of user fees for FDA review. In Aug. 2021, Project ALS announced plans for an early-stage clinical trial of prosetin, testing primarily for safety and optimal dose.
Erin Fleming, ProJenX co-founder and operations director says in a company statement released through Cision, “Prosetin was developed out of a decades-long collaboration between the labs of Hynek Wichterle and Brent R. Stockwell at Columbia University and Project ALS to build more predictive models of ALS, and then use them to identify better treatments. We have seen promising effects of prosetin in a range of laboratory models and are hopeful for its potential to improve the lives of many people with ALS and other devastating neurological conditions.”
Medical Excellence Capital is providing ProJenX with $5.1 million in seed funds as well as its managing partner Eric Heil to serve as interim CEO. Medical Excellence is an early-stage life sciences venture investor that formed and incubated ProJenX. With the funds, ProJenX plans to start clinical studies of prosetin, hire more executives, and support preclinical work on other therapies.
“Patients with ALS desperately need new therapies,” notes Heil. “We believe that the patient-specific, cell-based discovery platform at the heart of ProJenX’s approach is an exciting opportunity for the creation of transformative neuroscience medicines.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on February 15th, 2022  (Heung Soon, Pixabay. https://pixabay.com/photos/approximately-health-3887433/) 15 Feb. 2022. A late-stage clinical trial is underway testing an oral anti-viral drug to treat moderate to severe cases of Covid-19 infections. The drug, code-named LAU-7b, is made by Laurent Pharmaceuticals Inc. in Montreal, Quebec, Canada with a patient enrolled in the trial receiving the first dose of the drug or placebo.
Laurent Pharma develops treatments addressing lipids, or natural oils, making up the structure and functions of cell membranes. Those lipids, says the company, play key roles in cell defenses against pathogens and signaling presence of inflammation. Laurent Pharma says its technology targets lipids with various acidic compositions linked to pathogen defense, or the activation or resolution of inflammation.
To treat Covid-19 infections, says Laurent Pharma, LAU-7b uses a low-dose formulation of the cancer drug fenretinide that reduces fluidity and limits production of new lipids on cell membranes. As a result, invading SARS-CoV-2 viruses, enveloped with lipids, cannot restructure cell membrane lipids to enable their penetration and infection of host cells. And, says the company, since LAU-7b acts on host cells and not proteins in the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the drug can treat infections from a range of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Laurent Pharma says lab tests show LAU-7b stops SARS-CoV-2 gamma and delta variants, as well as the earlier Middle East Respiratory Syndrome or MERS-CoV coronavirus.
Hospitalized patients with moderate to severe Covid-19
“Existing Covid-19 oral antivirals typically target the virus’s biological machinery,” says Laurent Pharma vice-president Jean-Marie Houle in a company statement, “which can be eluded by mutations, and are effective only if taken within five days of symptoms onset, during the virus proliferation stage. LAU-7b has the potential to become the next generation pan-coronavirus oral pill, so we will never be caught off-guard again by this virus.”
The clinical trial is a combination mid- and late-stage study eventually recruiting 508 participants at 14 sites in the U.S. and Canada. Participants are hospitalized patients with moderate to severe cases of Covid-19 infections, randomly assigned to receive a daily LAU-7b or placebo capsule for 14 days. At that point participants are tracked for 60 days, looking primarily for changes on a seven-point disease status scale, from non-hospitalized with no limitations to deceased. The study team is particularly tracking rates for the two most severe outcomes: hospitalized with mechanical ventilation needed or death.
The mid-stage or phase 2 part of the study enrolled 148 participants, with none of the 76 LAU-7b recipients dying or requiring mechanical ventilation, while nine of the 72 placebo recipients required mechanical ventilation or died. By day 29, says the company, more LAU-7b than placebo recipients were alive and free of respiratory failure, with LAU-7b recipients also more likely to recover faster and leave the hospital earlier. The mid-stage findings allowed for the late-stage part of the trial to begin, with the first participant at Lumis Health in Annapolis, Maryland receiving an initial dose.
Laurent Pharma says it met with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration that cleared the company to begin the late-stage part of the trial. “We are excited to reach the Phase 3 development milestone and the positive feedback received from the FDA, confirming the progress made so far with our LAU-7b program in Covid-19.” notes company president and CEO Radu Pislariu. “There is still an important treatment gap for moderate-to-severe Covid-19 patients, the population most at-risk of progressing to respiratory failure.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on February 15th, 2022 – Contributed content –
 (TheDigitalWay, Pixabay) 15 Feb. 2022. Running a business is no easy task. From marketing and sales to product development and operations, there are many things to think about. It can be challenging to keep everything organized and under control. That’s where these four tips come in. Using them can get a tighter grip on your business operations and improve your efficiency. Let’s take a look at what they are.
Develop a clear and concise business plan
One of the most important things you can do to tighten up your operations is to develop a clear and concise business plan. This document will outline your company’s goals, strategies, and tactics, as well as how you plan on achieving them. Without a business plan, it will be much more difficult to stay on track and ensure that all aspects of your operation are running smoothly. So, take some time to sit down and map out your business strategy. Once you have a solid plan in place, you can start putting it into action!
Implement a CRM system
It’s hard to keep track of all your business contacts when you have hundreds or even thousands of them. A CRM system is a great way to organize these people into categories so that it’s easier for you to find what you’re looking for and get in touch with the right person at any time. You can also use this software as an email marketing tool since many offer templates and autoresponders, allowing you to send out mass messages without spending too much time on each one individually. Additionally, they’ll help ensure no important details are left behind during follow-up conversations by keeping notes about previous calls accessible right within their database (so long as there isn’t anything confidential).
Use accounting software
If you want to tighten up your operations, you must use accounting software. There are many different types out there, and some of them are better than others, so do your research before deciding which one will work best for your business. An excellent place to start is by looking at reviews online – this should give you an idea about how people feel about each product or service being offered in terms of price point and features like ease-of-use, payroll, and customer support availability (both live chat options).
Invest in training
Investing in training is another excellent way to tighten up your operations. Exercise will help you become more efficient and productive, which will lead to better results for both the company and customers alike. It’s also worth noting that when employees feel like they’re being taken care of by the management (and not just seen as replaceable cogs within an assembly line), there tends to be less turnover at work – meaning fewer costs associated with constantly hiring new people! So even though investing time into employee education initially may seem like it might cost money upfront, over time, these investments pay off because they reduce overall labor expenses while simultaneously increasing quality output from workers.
Using these four tips, you can get a tighter grip on your business operations and improve your efficiency. So don’t wait any longer – start putting them into action today.
* * *
By Alan, on February 15th, 2022 – Contributed content –
 (PhotoMix, Pexels. https://www.pexels.com/photo/turned-on-phone-displaying-collections-book-242492/) 15 Feb. 2022. Whatever your industry it will be subject to continuous change and development. New technology may be developed, new rules or regulations implemented, or groundbreaking news could be transforming the way in which your industry operates. Staying on top of industry news is essential and here why.
Avoid getting caught out
If you are not paying attention to industry trends and keeping on top of them you might soon appear to look out of date or even unprofessional in front of peers, colleagues, and clients.
Opportunities
With changes in any industry, it can bring with it new opportunities. It could be a result of a merger or restructure, it could be a result of new technology that changes the way you work or a change in the law that in turn puts an opportunity at your feet. If you are behind the times of developing industry trends you will miss out on potential opportunities.
Authority and respect
If you keep on top of emerging developments you will soon carve out a reputation as the person to go to for the answers. Your peers will respect your knowledge and intuition within your industry and in turn, this will give you a sense of authority and gravitas you might not have enjoyed before.
How to stay on top of industry news
The benefits of staying on your game are clear but how do you get yourself in that position in the first place? Below is a list of resources that can help you keep up to date with industry developments.
Blogs
Blogs can be a fantastic resource for keeping up to date with new developments in any industry. By reading relevant blogs you can benefit from the hard work the blogger has put into gathering, collating, and disseminating the new trends. To avoid missing hot of the press articles from your favorite bloggers ensure you subscribe to their blog to have fresh content delivered straight to your inbox.
Industry websites
Authoritative websites within a particular niche or industry are likely to have a section dedicated to news or even their own blogs, which disseminate important information. Visit https://kallibr.com.au/news/ for one such example. Keeping a close eye on industry leaders and announcements made via their website can be an effective method for keeping on top of the must-know developments.
Social media
Social media has fractured into many industries, niches, and for many purposes. Gone are the days when Facebook is just for sharing holiday snaps and Twitter liked your friend’s bad jokes. Nowadays Twitter can be an excellent way of keeping up to date on industry trends and developments. Experts in their field commonly take to Twitter to express opinions, news, or industry developments.
Another great tip is to follow the aforementioned bloggers’ social media accounts. Bloggers are notoriously vocal across social media and you will get an insight into what they are talking about and any new publications they have in the works.
* * *
By Alan, on February 14th, 2022  (National Cancer Institute, Unsplash) 14 Feb. 2021. A challenge competition is seeking computational biology teams to propose a new technology with artificial intelligence for enhancing antibody therapies. AION Labs in Rehovot, Israel — a coalition of pharma and technology companies in the U.S., Europe, and Israel — will provide the winning team with data for constructing A.I. models as well as funding and support to incubate the new company.
The challenge — called A.I. Enabled Design and Optimization of Antibodies for Targeted Therapies — seeks teams working in computational biology and chemistry to propose new ideas for a technology platform that enhances and optimizes antibody therapies in much less time than today. The competition is conducted by BioMed X, a research institute in Heidelberg, Germany that sponsors crowd-sourced studies in molecular biology, cell biology, computational biology, and diagnostics by early career scientists in academic labs and start-up companies.
BioMed X notes that antibody therapies are becoming treatments of choice for a number of diseases, including Covid-19 infections. But despite their emergence as leading treatment types, new antibodies often require long periods of time for discovery and optimization. The competition seeks new computational techniques for antibody design that optimizes therapeutic properties such as stability, aggregation, immune system response, chemical activity in the body, and tissue distribution. The technology should also enhance an antibody’s development and manufacturing capabilities.
The goal, says BioMed X, is a platform using A.I. that enhances existing antibodies, while cutting design time and iterations, and reducing attrition rates. An ideal end-to-end system would use protein binding sequences as targets to generate new variations of immunoglobulin G or IgG antibodies with the needed biological, physical, and targeting properties.
Initial proposals due in April
AION Labs is a collaboration of drug makers AstraZeneca, Merck, Pfizer, and Teva, with Amazon Web Services and the Israel Biotech Fund. The winning team will receive receive from AION Labs research funding of up to $2 million over four years and an equity stake for a start-up company, with computational and wet lab facilities and access to data repositories for developing algorithms in the proposed solution. The new company will be incubated at AION Labs with mentors from academia, industry, and venture capital.
Teams are asked to register and submit their three to five page proposals via BioMed X by 10 April 2022. A panel will review proposals and finalist candidates will be asked to take part in a five-day innovation camp in Israel in June. Participants in the camp will refine their proposals and make their pitches to a jury on the last day, followed by selection of the winning team.
“We’re anticipating another strong round of applications,” says AION Labs chief technology officer Yair Benita in a BioMed X statement, “and look forward to working together with the chosen startup to develop a cutting-edge solution to substantially improve the design and optimization of antibodies for targeted therapies.”
This is the third challenge offered by AION Labs, and the second competition involving antibodies. In October 2021, Science & Enterprise reported on AION Labs’ first competition, seeking a computational platform that allows for design of new antibodies to meet antigen structure and sequence specifications that bind to precise epitope, or antigen binding site, targets.
More from Science & Enterprise:
Disclosure: The author owns shares in Pfizer.
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
|
Welcome to Science & Enterprise Science and Enterprise is an online news service begun in 2010, created for researchers and business people interested in taking scientific knowledge to the marketplace.
On the site’s posts published six days a week, you find research discoveries destined to become new products and services, as well as news about finance, intellectual property, regulations, and employment.
|











 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts
You must be logged in to post a comment.