Subscribe for email alerts
Donate to Science & Enterprise
|
By Alan, on August 21st, 2023  (Gerd Altmann, Pixabay. https://pixabay.com/illustrations/dna-analysis-research-7024975/) 21 Aug. 2023. A company developing a drug delivery process with treatments activated by ultrasound received an option to license a key technology from its founders’ university labs. Suono Bio in Foxborough, Massachusetts says it has an exclusive option to license techniques devised for an oral capsule that responds to ultrasound for delivering nucleic acids, biologics, and other drugs to the lower digestive tract.
Suono Bio is a six year-old enterprise founded by biomedical engineering researchers at Mass. Institute of Technology to improve delivery of many treatments considered difficult to deliver through conventional means. The company’s founders, Robert Langer and Giovanni Traverso at MIT, study materials science, chemistry, and physiology for drug delivery, particularly for extending release of drugs over longer periods and delivering drug cargoes to the gut, a difficult region to reach because of stomach acids that can affect normal oral drugs.
The Suono Bio process uses focused ultrasound to create pressure variations that cause cavities to form in liquids. Those cavities fill with gases or vapors from the liquid that subsequently implode. When applied to therapies, such as biologic drugs or nucleic acids like messenger RNA, pressure variations can drive a therapy into the tissue lining the gut or other targets, where it penetrates into the tissue. In this case, ingestible capsules designed to survive the rigors of the digestive tract carry the active ingredients, where the capsule adjoins the mucous layer of the lower digestive tract, for activation by ultrasound to release the contents into gut tissue.
Safe and well tolerated with no adverse effects
Suono Bio says its preclinical studies demonstrate the feasibility of the process, including delivery of insulin that usually requires injections into live pigs. The company says that process can deliver a wide range of drug compounds, biologics, and nucleic acids. In July 2023, Suono Bio released results of tests of its lead product called SuonoCalm, given as a rectal suspension in an enema, then activated by ultrasound for treating ulcerative colitis, among healthy volunteers. The findings — not yet peer-reviewed — from tissue and blood samples, says the company, show the treatments are safe and well tolerated with no adverse effects.
The technology optioned from MIT applies to oral capsules activated by ultrasound for delivery of therapeutic cargoes into the lower digestive tract. An option to license gives a licensee an exclusive right to negotiate and enter into a long-term agreement with the inventor or owner. Details of the agreement with MIT, including financial terms, are not disclosed.
Suono Bio CEO Scott Kellogg says the process for ultrasound-activated ingested capsules will help the company expand its drug delivery options. “This agreement will allow us to expand our oral drug delivery program,” says Kellogg in a company statement released through BusinessWire, “with the potential to reach across a variety of potential indications.” Kellogg adds, “We have the distinct capacity to modulate where we deliver drug to, including intracellularly, which allows us to take a per-indication or asset approach to develop a new, broad range of oral therapeutics that could be utilized across a range of potential therapeutic solutions.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on August 19th, 2023 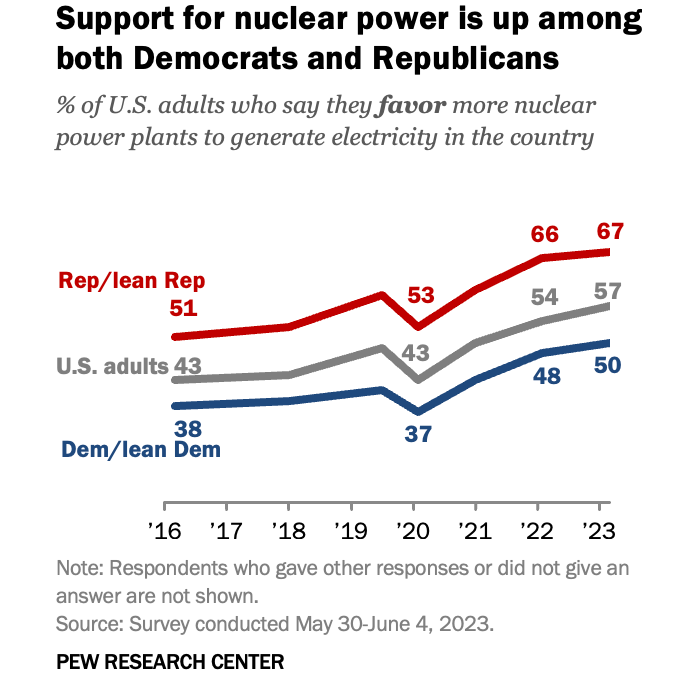 (Pew Research Center) 19 Aug. 2023. As the climate crisis focuses more attention on alternatives to fossil fuels, nuclear energy is gaining more popular support in the U.S. as one of those alternatives. The Pew Research Center reported the findings yesterday, from a survey conducted in May and June 2023, with at least half of respondents in both political parties favoring more nuclear power plants.
A majority of participants in the Pew Research poll (57%) say they favor more nuclear power plants to generate electricity in the U.S., with the proportion growing from a little more than four in 10 (43%) three years ago. Nonetheless, larger majorities of Americans still favor more use of solar power (82%) and wind energy (75%) as sources for generating electricity in the U.S. However, nuclear power emerges as the least divisive option across party lines in the U.S. Two-thirds (67%) of Republicans and independents leaning toward the GOP say they’re in favor of nuclear power to produce electricity, while half (50%) of Democrats and their independent friends agree.
And while majorities of Republicans and supporting independents also favor more solar and wind power — 70 and 60 percent respectively — they’re far outpaced by the nine in 10 Democrats and independent friends, 91 and 93 percent, supporting more solar and wind. In addition, solid majorities of professed and leaning Republicans, 63 to 73 percent, also favor continued coal, oil, and natural gas development in the U.S., compared to a quarter or less of Democrats and friends.
Pew Research Center conducted the survey online with 10,329 U.S. adults taking part in the Center’s American Trends Panel from 30 May to 4 June 2023. Participants are recruited through national random sampling of U.S. households, with results weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on August 18th, 2023  (Lynn Ketchum, Oregon State University, Flickr. https://flic.kr/p/Gh96nd) 18 Aug. 2023. A discoverer of neuroscience therapies and a genomics data science company are developing machine learning models to predict clinical trial outcomes for ADHD drugs. Financial and intellectual property details of the collaboration between 3Z Pharmaceuticals in Reykjavík, Iceland and biotx.ai in Potsdam, Germany — the company name is spelled in all lower-case — are not disclosed.
3Z Pharmaceuticals discovers new treatments for central nervous system disorders by screening existing drugs with genetic models in zebrafish, a tropical fish in the minnow family. Zebrafish have a 70 percent genetic similarity to humans, with an array of organs also similar to humans including brain and spinal cord. 3Z Pharma says zebrafish brains express the same neurotransmitters as humans, which allows for real-time live animal screening of drug candidates. The company says it tracks behaviors of genetically-engineered zebrafish affected by drugs, with models linking those behaviors to schizophrenia, Parkinson’s disease, sleep disorders, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder or ADHD.
3Z Pharma says it repurposes currently approved drugs since they often have known safety profiles, which require fewer early-stage clinical trials and thus faster market entry. The company now has four therapies for ADHD in its pipeline, with an insomnia treatment, all in preclinical stages.
Link clinical trial success to zebrafish screenings
biotx.ai is a six year-old enterprise building machine-learning models for identifying causal biomarkers for drug discovery. The company says its algorithms are based on data from 28,500 drugs and 2 million genomes linked to 12,000 diseases, and 500 disease-related traits. biotx.ai says its models run in the cloud with a capacity of one million experiments per day. The company works for drug makers and biotechnology companies to discover causal biomarkers to design clinical trials, repurpose existing drugs, and better understand therapies’ mechanisms of action. One of its customers is a developer of treatments for Alzheimer’s disease.
In their collaboration, biotx.ai and 3Z Pharmaceuticals seek to develop algorithms for predicting the clinical trial success of ADHD drug candidates from real-world data generated by zebrafish screenings. The companies expect the algorithms to be based on genomic models to predict likely effects on treating ADHD in patients, evaluate metabolic impacts, and assess effects on other disorders. The data will then predict outcomes in a simulated mid-stage clinical trial. 3Z Pharma believes the findings can reduce the risk of developing new uses for current drugs by finding direct links between preclinical animal tests and clinical trial results.
“We are entering a new era in drug discovery and development,” says 3Z Pharmaceuticals CEO Karl Karlsson in a company statement released through Cision, “where AI has the potential to revolutionize the industry. The animal models we develop focus on disorders and diseases that manifest as dysregulation within neuronal networks, which is probably the most challenging aspect to simulate successfully. However, we can model the effects of the drugs we identify on specific genetic targets, enabling us to obtain critical information and significantly reduce the risk of failure going forward.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on August 18th, 2023 – Contributed content –
 (Campaign Creators, Unsplash) 18 Aug. 2023. A lot of business owners know that technology can be useful, but they don’t quite know exactly how to use it or why it’s important. That means they’ll use just the bare minimum and could be missing out on a lot of benefits that would make their business run more smoothly and their lives (and the lives of their employees and customers) easier.
The fact is that technology is shaping and changing everything in business, from communication and marketing to data management and customer service, and it can be the difference between a successful business and one that has to fold quickly. It’s crucial for business owners to know much more about technology than they probably do right now, so they can use it to their advantage and create a business that can really be something special. With that in mind, here are some of the reasons why technology is needed in modern business; once you know what the reasons are, you’ll be able to implement it more successfully. Read on to find out more.
More Efficiency And Productivity
What do people – not just business owners – know about business? It’s that time is money, and anything that slows business down is costing you money, and anything that speeds it up and makes it more efficient is making you money. It sounds simple, and in essence, it is, but of course, finding those things that speed up your business is sometimes a challenge.
Technology can often be the answer. Using technology can help to streamline your business processes, automate tasks, and reduce mistakes as much as possible. These are all things that, if they’re not taken care of, can really cause problems in a business, and potentially cost you sales and lose you money.
Automation can be one of the best uses of technology if you want your business to be more productive because repetitive and time-consuming tasks aren’t the best use of your employees’ time, and it’s better to automate these things and have them work on other, more complex projects.
Collaboration and teamwork have also been transformed thanks to more technology in business. In the past, teams working on a project might have been restricted by their location, and remote working would have been a big problem. However, with cloud-based tools and platforms and communication apps at the ready, everyone can work together easily, whether they’re in the same room or in a different country.
These are just some examples of how technology can improve the efficiency of a business, and there are many more besides.
Improved Customer Engagement
Customers are at the heart of everything in business, and without them, there would be no business at all – that can be a scary thought, as it means you’ll have to work harder than you might have imagined to keep them happy and satisfied, and ensure they come back time and again to keep spending money with you.
It doesn’t have to be scary, though, when you use technology, and this is another great reason why it’s so important in business. Take marketing, for example; gone are the days of one-size-fits-all marketing ideas that try to speak to everyone, and it actually makes a lot more sense to tailor your marketing to your target audience. Technology can help with this is you use a customer relationship management (CRM) system, for example. This will give you all the insights you need about your customers, and you can make a marketing campaign that they’ll notice and pay attention to.
You can also use technology to keep in touch with your customers better. With the right tech, you can contact customers through email, social media, text messages, videos, and even direct mail. What you do will depend on what the customers like best (something else you can find out with plenty of market research), but having a variety of different methods to reach out with means you won’t miss anyone out, and you’ll stand the best chance of making more sales.
Chatbots are a piece of technology that has become very popular, and they’re extremely helpful for businesses and customers alike. With a chatbot, your customers can get answers to their more simple questions right away, so they won’t get frustrated and they might even decide to buy from you rather than looking for help somewhere else. Again, this is just one example of a piece of technology that can make customer engagement better, but no matter which ones you choose, the point is that when customers are happier, they’ll buy from you, come back to you, and tell their friends and family about you.
Keep Staff Happy
Although your customers are a major part of your business and will determine how successful you are in the end, something else that is hugely important is your staff. If they are good at what they do and can work in an efficient way, your customers will be happy, and the business is sure to grow.
You might not be surprised to find that if you want to keep your team happy, technology is the way to go. For one, it can mean you’re able to offer remote or hybrid working, giving people a better work-life balance and helping them be more productive – this isn’t something that would have been possible without good software and programs in place to let it happen. On top of that, your staff can learn more skills and develop their knowledge through online learning and training – the more they know, the more confident they’ll be, and that will give them high levels of job satisfaction.
You can also use technology to allocate work properly so that those with the right skills take on the right tasks, and you don’t overload people and cause burnout. Using something like field service management software, for example, will enable you to see exactly where your field team are, and what jobs they have to do. When a new task comes in, you’ll be able to give it to someone who doesn’t just have the right skills, but whose workload can accommodate it. Plus, you can even pick the person who’s closest to the customer who needs a visit, reducing travel time and costs and speeding up the work.
When you have a happy team, you can rely on them to do the work that needs to be done to grow your business and ensure it’s running as best it can. By using technology to make this happen, you can have a modern, progressive business with excellent and loyal staff.
Keep Your Business Secure
If you want to take care of your business and grow it for the long term, the last thing you’ll want is for anything to go wrong and for a theft to take place. Whether this is a physical theft and someone breaks into your office or warehouse, or a digital one and someone hacks into your computer network, the result will be the same – you’ll lose money, and you’ll have at least some downtime; you might have to close altogether.
Using technology to make your business more secure is a great idea and one that could save you a lot of heartache and financial strain. You can install high-tech security systems, for example, that record anyone who tries to get inside and send a message to the police or business owner so something can be done quickly. You can use security cameras and motion sensor lights. You can even have a smart building that requires fingerprints or retina recognition to let people in. And when it comes to cybersecurity, technology like firewalls, multi-factor authentication, encryption, and virus detectors will all play a part.
* * *
By Alan, on August 16th, 2023  Exosome illustration (NIH) 16 Aug. 2023. A clinical trial has begun testing an experimental treatment for burns using off-the-shelf therapeutic particles derived from human bone marrow stem cells. The study is sponsored and conducted by the biotechnology company Aegle Therapeutics Corp. in Woburn, Massachusetts, testing its biologic drug candidate code-named AGLE-102, developed for treating burns and rare skin disorders.
AGLE-102 is made of extracellular vesicles, also known as exosomes, tiny bubble-like particles emitted from cells, often carrying proteins or nucleic acids like DNA or RNA to nearby cells in the body. In this case, the extracellular vesicles are released by mesenchymal stem cells, so-called adult stem cells found in bone marrow that transform into connective tissue cells, including those found in bone, cartilage, muscle, and fat. The Aegle Therapeutics process is based on research by its scientific founder Evangelos Badiavas, professor of dermatology at University of Miami medical school, who studies mesenchymal stem cells as treatments for burns and other chronic wounds.
Aegle Therapeutics says extracellular vesicles emitted by mesenchymal stem cells contain messenger and micro-RNA molecules that promote paracrine signaling, which sends growth factor proteins to nearby cells. The company says its extracellular vesicles also transfer two types of collagen proteins needed for developing skin membranes, and unlike earlier attempts, are designed to promote healing without scarring or inflammatory responses. In addition, says Aegle, its process makes possible allogeneic or off-the-shelf nanoscale particles from extracellular vesicles derived from donated mesenchymal stem cells that go into AGLE-102 and other therapies.
Measure burn wound closure and skin regeneration
The company says the first patient in the early- and mid-stage clinical trial received a dose of AGLE-102. The study is enrolling 10 patients at two sites with deep second-degree burns, the most common type of burns that cause blisters, discolored or shiny skin, and pain. Participants are treated with AGLE-102 within 48 hours of the injury, then two more treatments about one and two weeks later. The trial has no control or comparison group.
The study team is looking primarily for adverse effects from AGLE-102 for up to a year following the treatments. The researchers are also measuring closure of burn wounds and other indicators of skin tissue regeneration, such as restoring pigmentation and hair growth, at eight weeks following treatment. And, the team is assessing blood pressure rates in participants’ treated and unburned skin with Doppler laser, for up to a year following treatments.
“This milestone,” says Aegle Therapeutics CEO Shelley Hartman in a company statement released through Cision, “highlights our commitment to advancing extracellular therapy as an important multi-faceted approach to treating severe dermatological and immune based conditions.” The company plans a similar clinical trial for AGLE-102 as a treatment for epidermolysis bullosa, a rare inherited disorder where skin is fragile and easily blisters, in the fourth quarter of 2023.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on August 15th, 2023  (Vitaly Vlasov, Pexels) 15 Aug. 2023. Data scientists and cancer specialists demonstrate a data encryption technique that makes possible real-world cancer data sharing while preserving individual privacy. A team from the company Duality Technologies Inc. in Hoboken, New Jersey with cancer specialists and data scientists from academic labs present their findings in the 7 Aug. issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The researchers are seeking a solution for sharing a wealth of real-world health data amassed in individuals’ electronic health and insurance claim records that can improve medical decision-making for individuals and communities. While clinical trials can answer questions of efficacy and safety for new therapies and medical devices under controlled conditions, real-world health data offer a large base of user experience to help validate clinical data and provide insights beyond the limited numbers of patients enrolled in trials. But, say the authors, real-world health data are often found in fragmented, incompatible databases where many patients are reluctant to share their records.
Duality Technologies is a seven year-old company providing data security solutions for artificial intelligence in a number of industries including health care. The company’s process is based on research by its founders in computer science and engineering labs at University of California in Berkeley, New Jersey Institute of Technology, and MIT that Duality Tech says makes possible the capture of data from a wide range of databases, particularly for training machine learning algorithms. The company says its technology ensures owners of the original data keep control of their assets, while still enabling the integration of previously separate databases and use of complex statistics.
Genomic data difficult to de-identify
One of Duality Tech’s prime applications is analysis of real-world medical data often generated from multiple sources. In the new PNAS paper, researchers in computer science, engineering, and oncology from UC-Berkeley, MIT, UC-San Diego, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center in Israel, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, affiliated with Harvard Medical School, joined colleagues from Duality Tech to seek a solution for integrating real-world data from cancer patients while preserving the privacy of those records. The authors note that many current methods for de-identification of real-world medical records are labor intensive and difficult to scale, with genomic data particularly difficult to de-identify without losing important details.
The team applied a technique called fully homomorphic encryption or FHE that adds an encryption layer to already encrypted data, thus removing a need for a decryption key to the underlying data records. The authors enhanced FHE with a collaboration model where parties can temporarily contribute data to matched records for further analysis, and extended their privacy tools to statistics often employed in cancer research.
The researchers tested their techniques on real-world electronic health records of colorectal cancer patients at Sourasky Medical Center and data from two clinical trials of immunotherapy drugs among kidney cancer patients. The team found they could apply FHE with multi-party enhancements to process data with a number different statistical analytics from previously incompatible databases, without revealing the underlying raw records. And, say the authors, the techniques scale well to larger databases and can be applied to other collaborative health research tasks.
“Our joint study with Duality,” says Ravit Geva, head of clinical research in oncology at Sourasky Medical Center and the paper’s first author in a Duality Technologies statement released through Cision, “aimed and verified the accuracy of statistical oncology endpoints when done through encrypted data. The secure analysis yields accurate results compared with the currently used conventional data management and analysis methods on collaborative real-world oncological analyses without revealing patients’ protected health information.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on August 14th, 2023  (NIH.gov) 14 Aug. 2023. A developer of electronic health data tools and a university’s neuroscience labs are collaborating on tests of Parkinson’s disease drugs using digital measures of patient functioning. The partnership brings together digital biomarkers company Koneksa Health in New York and researchers at Oregon Health and Science University in Portland.
Koneksa Health is an eight year-old enterprise creating data collection instruments, particularly for remote data capture, in clinical trials and other medical studies. The company says many of its digital health tools use passive and unobtrusive measures to gain more objective and reliable data than conventional self-reporting methods impaired by personal biases and reliance on human memory. Koneksa says it focuses on collection tools incorporated into mobile and portable devices used at home, along with electronic patient-reported outcomes or ePROs, connected to analytical algorithms. The company offers its digital biomarkers software as a cloud-based service for use by clinical trial sponsors and health research teams.
Most of Koneksa Health’s digital biomarkers are in neuroscience, which combine basic health data such as vital signs, with sleep and exercise data , and measures of physical activity directly related to neuro-motor functions: speech, gait, balance, tremors, and finger dexterity. In June 2023, Science & Enterprise reported on a Koneksa collaboration with Beacon Health, a company writing algorithms to analyze electroencephalogram or EEG data on brain activity, using a home wearable device.
Neuro-physiological indicators affected by Parkinson’s disease drugs
The new collaboration links Koneksa with OHSU researchers studying Parkinson’s disease, a degenerative and progressive disorder where cells in the brain cease producing dopamine, a neurotransmitter chemical that coordinates muscle movements. People with Parkinson’s disease experience tremors, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems, along with depression, memory problems, and other non-movement symptoms. OHSU neurologist Delaram Safarpour is leading the study with Martina Mancini, director of the university’s Balance Disorders Laboratory.
The study is assessing neuro-physiological indicators affected by common drugs treating Parkinson’s disease either released immediately into the body, or formulated for extended release over time. The researchers plan to use digital biomarkers developed by Koneksa to gauge responses by patients to the drugs, including measures of gait performance, taken every 30 minutes for four hours during office visits, as well as unobtrusive actigraphy indicators — measures of activity and rest cycles — captured by patients’ smartphones at other times.
“We’ll be including smartphone- and actigraphy-based digital measures and electronic patient reported outcome or ePRO instruments into our study,” notes OHSU’s Manicini in a Koneksa statement released through BusinessWire, adding “Novel, objective metrics, like those made possible with Koneksa’s technology and toolkit, allow us to expand upon what we’ve been able to do in the clinic.”
“These measures will support OHSU in both in-clinic and at-home patient monitoring of critical parameters of interest for this study,” says John Wagner, Koneksa’s chief medical officer. Koneksa expects the joint effort with OHSU to be the first in a series of collaborations with academic labs on Parkinson’s disease, using the company’s data collection measures for neuroscience. The company says it offers its digital biomarker tools, training materials for clinical site administrators, and cloud-based monitoring and algorithms for analysis.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on August 12th, 2023 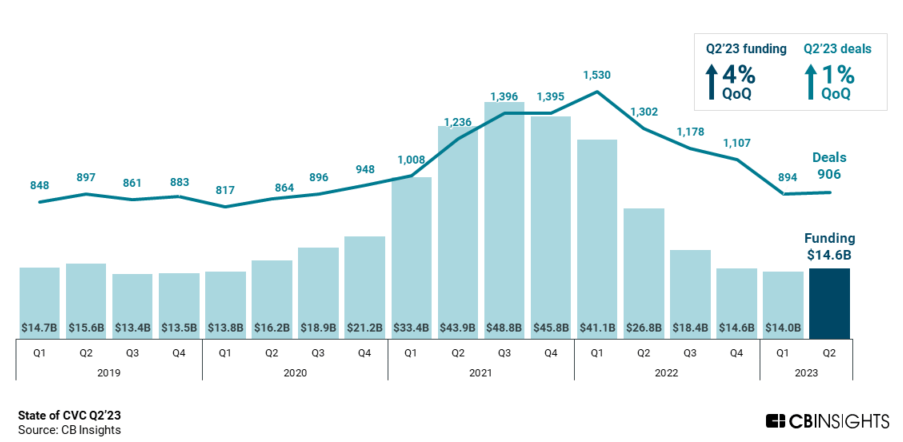 Click on image for full-size view (CB Insights) 12 Aug. 2023. Since the start of 2021, most news has been gloomy about venture investments, but a report last week suggests corporate venture capital funding worldwide is picking up. According to technology intelligence company CB Insights (registration required), venture capital funds managed by large corporations increased both in the total dollars invested in tech start-ups and number of deals in the second quarter of 2023.
Data from CB Insights show corporate venture capital funds invested $14.6 billion in tech start-up companies worldwide from April through June 2023, a gain of four percent from the first quarter of the year, the first quarterly gain since the third quarter of 2021. And the number of global deals by corporate venture funds also increased but by a smaller one percent, to 906 in the second quarter, the first rise since Q1 2022.
But before we celebrate too much, gains in corporate venture investing were uneven in Q2 2023. Total corporate venture fund dollars invested in U.S. start-ups fell 11 percent to $7.3 billion, the lowest quarterly total the third quarter of 2019. And the median size of corporate venture deals is also down so far in 2023 to $8.4 million, from $10 million for all of 2022. The smaller-size deals are felt across all company-round stages, from early to late-stage investments.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on August 11th, 2023  (Dariusz Sankowski, Pixabay. https://pixabay.com/photos/iphone-6s-plus-iwatch-apple-white-1032783/) 11 Aug. 2023. Findings from two clinical trials show a digital health mobile app helps improve outcomes and manage the conditions for people with depression and asthma. Results of the trials, conducted by Juli Health, developer of the juli app — the name is spelled in all lower-case — appear in separate postings on the pre-print server medRxiv and are not yet peer-reviewed.
The juli app, says Juli Health, provides users with a single platform for recording data and experiences related to chronic conditions including asthma, migraine, depression, bipolar disorder, hypertension, and chronic pain. The app combines health, activity, and wellness data gathered passively from Apple phones and watches, with data entered by users on their medications, mood, and related factors, and with third-party reports on weather, pollen, and air pollution. The app also engages users through Q&A chat and game features to gain more insights.
The juli app, available only for the iPhone, integrates with Apple Health to capture data from phones and watches. The collected data, says the company, are processed with artificial intelligence algorithms to provide feedback and guidance to encourage a series of micro-level behavioral changes among users related to their health conditions.
A team from Juli Health and University College London assessed the app in two separate clinical trials among users with depression and asthma. The first trial enrolled 908 adult participants who self-identified with depression and scored above a specified threshold on a standard patient health questionnaire. Participants were randomly assigned to use either the full juli app or a limited/placebo app that asked only about the user’s overall condition each day, for eight weeks.
Gains on primary measures in both trials
The researchers looked mainly for changes in depression scores on the standard health questionnaire, but also on other depression-state and quality of life indexes, with 456 participants completing the trial. Results show participants using the juli app record lower depression scores on the patient health questionnaire than limited-app users, with differences large enough for statistical reliability. The data show statistically reliable reductions in some, but not all, secondary depression health and quality-of-life scores.
The second trial recruited 411 adult participants self-reported with asthma, and scoring low on an index-test for controlling their asthma. As in the first trial, participants were randomly assigned to use either the juli app for eight weeks, or a limited/placebo app that asked only about daily general well-being. After two weeks, 262 participants were still in the trial, enabling some partial analyzes, with 152 participants completing the trial.
The study team looked primarily for changes in participants’ scores on the asthma control test, but also for scores on related asthma condition measures and quality of life. The findings show after eight weeks, juli app users score higher on the asthma control test than limited-app users, with statistically reliable differences. Differences in other measures of asthma control and quality of life, however, are not large enough for statistical reliability.
“Our studies not only demonstrate the effectiveness of the platform,” says Joseph Hayes, professor of psychiatry at University College London, Juli Health co-founder, and senior author of both studies in a company statement released through Cision, “they also show that juli works across the very different conditions of asthma and depression, validating our approach to cover multiple chronic conditions, including their comorbidities.”
Juli Health is a three year-old enterprise based in Boston. In Mar. 2022, Science & Enterprise reported on the company raising $3.8 million in seed funds.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on August 9th, 2023  (GDJ, Pixabay. https://pixabay.com/vectors/wave-waveform-aural-audio-sonic-1837426/) 9 Aug. 2023. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, a maker of synthetic biologic treatments, is acquiring Decibel Therapeutics, developer of gene therapies to treat hearing loss and balance disorders. The deal is expected to bring Decibel Therapeutics shareholders as much as $213 million if all terms of the agreement are fulfilled.
Decibel Therapeutics is an eight year-old biotechnology enterprise founded by researchers in neuroscience and speech and hearing anatomy at Harvard Medical School, Johns Hopkins University, and University of Michigan. The research behind the company’s technology identifies genetic variations associated with hearing loss and balance disorders, often linked to the aging process or injury. In this case, however, Decibel seeks to restore normal hearing and balance by transferring functioning genes to regenerate sensory tissue and hair cells in the cochlea, the spiral section of the inner ear where sound waves are converted into nerve impulses.
The company says its process aims to model the development of human cells involved in hearing and balance. Decibel says it isolates genetic activity at a granular single-cell resolution, then with the aid of bioinformatics, designs treatments that regenerate progenitor cells into sensory tissue and hair cells to restore normal hearing and balance. For example, outer hair cells in the ear act as amplifiers of sound into the ear, but are often lost as a result of aging. Restoring outer hair cells is one of Decibel’s treatment objectives.
Mutations associated with inherited hearing loss
Decibel Therapeutics also addresses hearing loss from genetic causes in children. The company’s lead product, code-named DB-OTO is a gene therapy addressing mutations in the otoferlin gene, where alterations are associated with inherited deafness. An early- and mid-stage clinical trial of DB-OTO is set to begin, enrolling 22 children, including infants, in the U.S., Spain, and the U.K. with profound hearing loss and otoferlin gene mutations. The study aims to determine safety and dosage levels of the treatments, but the team is also tracking changes in hearing thresholds and auditory brainstem responses in participants.
Regeneron Pharma and Decibel Therapeutics are hardly strangers. Regeneron and Decibel are collaborating on development of DB-OTO and two other gene therapies for inherited hearing loss, a relationship begun in 2017 and renewed in 2021. “DB-OTO, our shared lead investigational gene therapy,” says Regeneron president and chief scientist George Yancopoulos in a statement, “will soon reach patients in its first clinical trial, offering new promise to children with this rare form of congenital hearing loss, as well as potential proof-of-concept for future gene therapies addressing more common forms of genetic hearing loss.”
Regeneron is acquiring Decibel Therapeutics by purchasing current Decibel shares for $109 million or $4.00 a share. Further payments to shareholders are contingent on Decibel achieving specified product development milestones, such as progress on DB-OTO clinical trials, and acceptance of biologics license applications or the equivalent in the U.S. and Europe. Achievement of the milestones are expected to add equity value of $104 million to shareholders.
“We at Decibel are deeply committed to discovering and advancing innovative new therapies with the potential to be transformative for people with severe forms of hearing loss,” notes Laurence Reid, Decibel Therapeutics CEO, who adds that “this transaction is the best way to maximize shareholder value and ultimately benefit patients.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
|
Welcome to Science & Enterprise Science and Enterprise is an online news service begun in 2010, created for researchers and business people interested in taking scientific knowledge to the marketplace.
On the site’s posts published six days a week, you find research discoveries destined to become new products and services, as well as news about finance, intellectual property, regulations, and employment.
|











 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts
You must be logged in to post a comment.