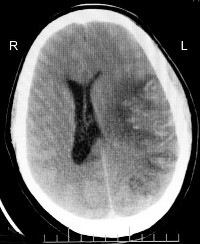
Researchers at the Institute for Neurological Research in Los Angeles, California report reductions in brain inflammation and neurological disabilities in stroke victims after administration of the drug etanercept. The proof-of-concept research was published in the 1 February 2011 issue of the journal CNS Drugs (paid subscription requried).
Etanercept is a drug that blocks tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) for treating inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. TNF alpha is a protein produced in the body as reaction to injury, which initiates and amplifies the inflammation.
In this study, three patients who had suffered a stroke between 13 and 36 months earlier, received an injection of etanercept and within 10 minutes began showing changes. The researchers found improvements in weakness and sensory deficits on one side of the body, gait, hand function, spatial perception, speech, and cognition. The patients received a second injection 22 to 26 days after the first dose, and further clinical improvements were noted.
The researchers released a video showing before-and-after results of the etanercept treatments.
* * *

 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts
[…] Read more: Drug Reduces Stroke Victim Brain Inflammation, Disability […]
[…] Read more: Drug Reduces Stroke Victim Brain Inflammation, Disability […]
any further stroke research done with this drug?
Thanks for your comment and readership of Science Business. Here’s the link to the current list of clinical trials on Etanercept. If any trials deal with stroke, they should be in there. – Alan
[…] Read more: Drug Reduces Stroke Victim Brain Inflammation, Disability […]
I am very interested in the etanercept treatment for stroke victims. My father had a stroke about 6 months ago and then cranial surgery to relieve pressure from a blood clot between his skull and brain. His eye sight a lot worse after the stroke in addition to his short term memory. Is there a list of doctors that perform this procedure or is it even available yet?
Thanks for any info.
Thank you William for your comment and visiting Science Business. Our story about etanercept treatments ran nearly two years ago, and reported on a proof-of-concept study. You can contact Institute of Neurological Recovery to see if they are in clinical trials for the treatment. The institute has an online request for consultation form at http://www.strokebreakthrough.com/request-consultation/ . The telephone numbers are 310-824-6199 in Los Angeles or 561-353-9707 in Boca Raton, Florida. Good luck. -AK