Subscribe for email alerts
Donate to Science & Enterprise
|
By Alan, on July 28th, 2023  (Ildar Sagdejev, Wikimedia Commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:2008-03-14_Ambulance_on_Luckie_St.jpg) 28 July 2023. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued new regulatory guidance for clinical trials of medical devices designed to prevent or treat opioid use disorder. The agency released the draft document in the Federal Register for 90 days seeking public comments, outlining issues regulators want to see addressed in clinical studies of medical devices offering help for people with opioid use disorder.
The opioid crisis in the U.S. continues with deaths from drug overdoses increasing over the past 20 years, and accelerating since 2013. The recent jump in overdose deaths can be traced to synthetic opioid compounds such as fentanyl. Center for Disease Control and Prevention says synthetic opioids have largely replaced prescription pain drugs and heroin among people with drug overdoses. In one year, from 2019 to 2020 says CDC, deaths from prescription opioids and heroin rose 17 percent and 7 percent respectively, while overdose deaths from fentanyl and other synthetic opioids rose 56 percent.
While medications such as naloxone are being fast-tracked in regulatory reviews as a rescue drug for opioid overdose — FDA today also approved a second non-prescription/over-the-counter naloxone nasal spray — the agency is also encouraging medical device developers to address the problem. For example, in 2018, FDA began a challenge competition for medical devices to help people deal with opioid addictions, resulting in more than 250 responses and eight finalists with technologies for diagnostics, monitoring, therapies for opioid use disorder or alternative pain treatments, and medication dispensing.
Follow-up periods of at least six months
The new FDA guidance seeks to spell out key issues for developers designing clinical trials assessing their medical devices to prevent or treat opioid use disorder. Diagnostics and alternative pain treatments are outside the document’s scope. In testing the efficacy of therapy devices, the guidance recommends developers use sham devices, replicas of test symptoms with therapeutic actions removed, in comparison or control groups. The document also recommends follow-up periods of at least six months, due to risks of relapse among study populations, as well as taking steps to retain trial participants and account for missing data.
FDA proposes medical device developers employ tight assessments of trial participant drug use in clinical trials, both prescribed and non-prescribed drugs. While participants may be asked to self-report on their drug use during clinical trials, the guidance recommends device developers also run scheduled and random drug tests with urine or other fluid samples. Changes in drug use patterns are often primary indicators of efficacy, says the agency, thus reductions in drug use should be measured and reported as sample percentages, not as group averages.
When designing primary efficacy indicators, says FDA, developers should use criteria for describing symptoms of moderate to severe opioid use disorder, as defined in the latest (5th edition) of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, published by American Psychiatric Association. And the document calls for efficacy measures to include rates of adverse outcomes, such as need for emergency medical attention, incidence of hepatitis C common among drug users sharing needles, and participant deaths.
“We are committed to helping industry develop solutions that are proven to be effective to address the devastation caused by the overdose crisis,” says FDA commissioner Robert Califf in an agency statement. “This draft guidance for device studies should prompt industry to collect more comprehensive, timely, and diverse data to support device submissions that may help improve the lives of those with opioid use disorder.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on July 27th, 2023  Sickle cells illustration (Open Stax College, Wikimedia commons, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1911_Sickle_Cells.jpg) 27 July 2023. A group of academic and industry researchers exhibited in lab cells and mice a more direct delivery technique that could make gene therapies more accessible and inexpensive. Researchers from University of Pennsylvania medical school in Philadelphia, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and the biotechnology company Acuitas Therapeutics in Vancouver, British Columbia describe their process in today’s issue of the journal Science (paid subscription required).
A team led by pediatric geneticist Stefano Rivella of Children’s Hospital and UPenn cell biologist Hamideh Parhiz are seeking to make gene therapies and gene-editing treatments more feasible, as well as bone marrow transplant therapies overall. In most cases, gene therapies or transplants into bone marrow require transferring hematopoietic or blood-forming stem cells from healthy matched donors or the patient’s own modified stem cells. But this process, called myeloablation, requires extensive conditioning of the recipient’s bone marrow, generally with chemotherapy or radiation, to make room for the transplanted cells or therapies, a risky process for many patients.
The researchers in this study demonstrate an alternative approach for delivering gene therapies or healthy stem cells to bone marrow that skips a separate conditioning step and makes possible a more straightforward transfer method. The team adapted nanoscale lipid or natural oil particles to deliver messenger RNA or mRNA, synthesized nucleic acid with protein-making instructions transcribed from DNA, a technique used in vaccines protecting against Covid-19 disease. In this case, the lipid nanoparticles target receptor proteins for CD117, a gene that plays a key role in formation of blood stem cells, with an antibody that conditions recipient bone marrow cells.
Lipid nanoparticles deliver gene-editing payloads
The team demonstrated an in vivo or inside-the-body conditioning process in lab mice, with a single injection of lipid nanoparticles carrying mRNA coding for the CD117-targeting antibody. The results show the lipid nanoparticles deliver their antibody payloads and condition blood-forming cells in mice, without chemotherapy or radiation. In a separate lab test, researchers delivered gene-editing RNA in lipid nanoparticles to blood samples from four individuals with sickle cell disease. Here, findings indicate lipid nanoparticles can deliver the gene-editing payloads to correct defects responsible for the disease, resulting in almost a complete absence of the malformed red blood cells.
“Right now, if you want to treat hematologic diseases like sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia with gene therapy,” says Rivella in a Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia statement released through Cision, “patients must receive conditioning treatments like chemotherapy to make space for the new, corrected blood cells, which is both expensive and comes with risks. In our paper, we have shown that it is possible to replace diseased blood cells with corrected ones directly within the body in a ‘one-and-done’ therapy, eliminating the need for myeloablative conditioning treatments and streamlining the delivery of these potentially life-changing treatments.”
Acuitas Therapeutics provided two participants for the study team. The company develops synthetic lipid nanoparticles for vaccines and therapeutics, including delivery of mRNA. The paper indicates, however, that University of Pennsylvania filed for a series of patents on the technologies in the paper between Dec. 2022 and May 2023, including gene editing of blood-forming stem cells with lipid nanoparticles and in vivo conditioning of blood-forming cells with mRNA delivered by lipid nanoparticles.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on July 26th, 2023  (Gordon Johnson, Pixabay) 26 July 2023. A treatment for depression designed as a game for patients will be assessed in a clinical trial conducted by a university psychology lab and funded by National Institutes of Health. The study, led by mental health professor Christopher Beevers at University of Texas in Austin, is evaluating the therapeutic game code-named ABM-02 developed by Arcade Therapeutics Inc. in New York.
Arcade Therapeutics is a four year-old company, originally named Wise Therapeutics, seeking to make it easier for people with mental health disorders to get help for their conditions, by applying advances in digital health and mobile gaming. The company’s core technology aims to address the greater attention and perceptions of threats by people with anxiety or depression, using games that modify cognitive processes underlying these negative patterns. The games employ a therapy technique called attention bias modification developed in tandem with greater access to mobile computing, and adapted with algorithms by the company to meet individual treatment needs and game-playing patterns.
Arcade Therapeutics’ lead product is StarStarter Rx that uses mobile games with attention bias modification or ABM in a digital therapy for social anxiety disorder. Recent research funded by National Institute of Mental Health, part of NIH, offers evidence that attention bias modification can also engage patients to reduce attention to threats, and encourage cognitive changes for reducing symptoms of major depressive disorder or MDD, a serious mood condition. Depression is treated in most cases today with psychotherapy, medications, or both.
Track depression symptoms over six months
The clinical trial, conducted by Beevers and colleagues at UT-Austin, is enrolling 600 individuals with major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to receive attention bias modification therapy in game form with ABM-02, attention bias modification through conventional psychotherapy, or a sham therapy that looks like attention bias modification. The study team plans to assess participants’ symptoms of depression periodically over six months, seeking evidence of progress, if any, over that time. National Institute of Mental Health is funding the trial, with $3.8 million over five years.
“We’ve known for decades that the tendency to focus too much on sad or dysphoric information drives and exacerbates symptoms of MDD,” says Beevers in an Arcade Therapeutics statement released through Cision. “Game-based ABM has the potential to effectively reduce this tendency, and thus MDD symptom severity, while also being highly accessible, scalable, and engaging to its users as a non-pharmacologic treatment option.”
Tracy Dennis-Tiwary, company co-founder and chief scientist, notes a game like ABM-02 can also help reduce the stigma that often hinders people with depression getting treatment. “Only half of those suffering from depression seek and receive treatment,” says Dennis-Tiwary adding, “Along with accessibility, one of the biggest barriers to receiving mental health treatment is stigma. By taking a clinically validated, game-based approach, ABM-02 not only radically improves accessibility, but reduces the stigma of seeking treatment for mental illness and meets patients where they are.”
More from Science and Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on July 25th, 2023  Knee joint X-ray (AKha, Wikimedia Commons) 25 July 2023. A biotechnology company creating living tissue from a person’s stem cells says it received FDA clearance for a clinical trial of its replacement knee cartilage. EpiBone Inc. in Jersey City, New Jersey — a spin-off enterprise from biomedical engineering labs at Columbia University — expects the study to begin in early 2024.
EpiBone says its process creates cartilage grafts for people needing new knee cartilage from sports injuries or other trauma, and arthritis resulting from knee trauma. The company says current tissue engineering techniques use cartilage samples from deceased donors, which while effective, can help a relatively few patients due to donation shortages. EpiBone says its technology that uses stem cells from patients to seed and cultivate replacement tissue, reduces risks of possible disease transmission or mismatched tissue from donors.
That technology, says EpiBone, starts with a precisely measured, personalized scaffold infused with stem cells in this case from bone marrow. The scaffold with stem cells are placed in a bioreactor, where the stem cells transform into cartilage cells, then multiply into new tissue forming around the scaffold. The bioreactor provides nourishment and controls the environment for stem cells to differentiate or mature into working tissue. When fully formed, the new cartilage can then be surgically implanted in the patient.
Better integration with surrounding tissue
The company released results of a preclinical study with horses conducted by Cornell University and reported in April 2023 at a meeting of the International Cartilage Regeneration and Joint Preservation Society in Nice, France. The study compared lab-grown cartilage tissue from the animals’ bone marrow stem cells to cartilage produced from donated cadaver tissue. The findings, says lead investigator and Cornell veterinary medicine professor Lisa Fortier, show similar performance results, but the lab-grown cartilage integrates better with surrounding tissue.
EpiBone co-founder and CEO Nina Tandon expects the company’s cartilage technology to first benefit younger people with sports injuries, “who need their knees to function for many years to come.” Tandon notes in a company statement released through Cision, “With this lab-grown living cartilage, we are able to offer patients a new avenue to harness the power of living cells to help cartilage heal when it normally is notoriously slow to recover from injury, if it recovers at all.”
According to EpiBone, the Food and Drug Administration cleared the company’s investigational new drug application or IND, in effect authorizing EpiBone to begin a clinical trial of its lab-grown cartilage. No further details of that clinical trial are yet disclosed. The company’s lead product, engineered bone tissue produced from a patient’s adipose or fat stem cells for facial reconstruction, is in an early- and mid-stage clinical trial.
Science & Enterprise reported in June 2016 on publication of preclinical findings showing the feasibility of lab-grown facial bone tissue from stem cells that precisely fits the defects and after six months integrates with host facial bones. The study was led by Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic, biomedical engineering professor at Columbia University and a co-founder of EpiBone with Tandon and first author Sarindr Bhumiratana, now the company’s chief scientist.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on July 25th, 2023 – Contributed content –
 (Fauxels, Pexels. https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-people-near-wooden-table-3184418/) 25 July 2023. If you want to start creating a successful growth strategy, you’ve got to start embedding a sense of togetherness with your teams. The concept of team value is something that we should remember is critical to productivity, engagement, and staff retention. While there are many different ways to make sure your team feels valued, here are some of the best:
Offer the Perks
It’s important to remember that if you want your team to work together effectively and improve autonomy, you have to give them the things that actually make them feel secure in the role. Paid time off is something that every business should offer in some capacity, and while those beginner companies may wonder how does paid time off work for them, if they can start to create an enticing holiday package, this will give your team a greater sense of security. Employees who have very little holiday and very little pay, as well as those that work freelance for companies, may not feel part of the team because they’re not being given the things that offer them a sense of fairness, especially if the company is paying full-time staff a great wage and providing sufficient holiday. An organization should foster team spirit even for those that are working by themselves, and this is where the perks will make a massive difference.
Express Gratitude
A very basic thing, but expressing your gratitude for the work your team does will ensure they feel valued. Gratitude is not just about thanking people once in a blue moon, but it’s about highlighting regular gratitude and specific gratitude to show your workers that it is genuine positive feedback. You can express your gratitude if a team is pulling together in the right direction to complete one major task, but also smaller doses of gratitude for day-to-day achievements also work very well. There’s a number of ways to showcase gratitude, whether it’s a simple thank-you email or something a lot bigger than that, for example, pizza!
Don’t Just Focus on Success
We have to reward efforts, not just the final product. One of the most demoralizing aspects of a workplace is when the focus is purely on what the end result is. It’s important that your team sees you value the efforts they are putting in, even if the goal is a long way off. A very simple morale builder, but it will ensure that they feel better in doing the work and will be more productive while they are doing it.
Positive Feedback
It’s essential to pass on positive feedback if you notice someone doing something well. Organizations that don’t give positive feedback to their employees run the risk of alienating them because those employees don’t know where they stand. If you notice a team member doing well, offering very supportive and constructive feedback will stimulate a bit more allegiance to the team as well as the business.
If you want to make your team feel better, you’ve got to make sure they feel valued. As simple as this is, there are many organizations that don’t value their employees in their droves. It’s time to start changing this.
* * *
By Alan, on July 24th, 2023  (Jeffy, Pixabay. https://pixabay.com/photos/pregnant-woman-pregnancy-stomach-1024884/) 24 July 2023. A digital health company with an app for monitoring maternal health is receiving nearly $1 million to add an algorithm for detecting a dangerous pregnancy complication. National Science Foundation last month awarded $975,000 to Emagine Solutions Technology in Tucson, Arizona for upgrading The Journey Pregnancy App developed by the company, with a machine learning model to predict preeclampsia in pregnant or post-partum women.
Preeclampsia is a form of high blood pressure during pregnancy, accompanied by high levels of proteins in urine indicating kidney damage. The disorder usually appears after 20 weeks of pregnancy or after birth, many times in women without a previous history of high blood pressure. In pregnant women, diagnosis of preeclampsia may require early delivery of the baby, depending on severity of the disease and stage of pregnancy. If left untreated, preeclampsia can result in life-threatening complications for mother and baby.
Preeclampsia occurs in two to eight percent of pregnancy-related complications, leading to as many as a 26 percent of maternal deaths in low-income countries and 16 percent in higher-income counties. Emagine Solutions cites data showing preeclampsia affects one in 20 births, or 150,000 women each year in the U.S. Data from the Kaiser Family Foundation show maternal mortality rates in the U.S. far exceed other advanced countries, particularly among people of color who often face unequal treatment from health care providers.
The Journey Pregnancy App is free to download and available for both iPhone and Android devices. The app tracks vital signs and other indicators such as blood pressure, glucose level, mood, and weight throughout pregnancy, alerts mothers if readings are out of range or reaching dangerous levels, and enables sharing of data with health care providers. Premium versions of the app provide for wellness coaching, health monitoring devices, and monthly reports.
The NSF award supports development of a machine learning model for pregnancy health that interacts with electronic health records systems. The proposed work calls for implementing the A.I. model to predict preeclampsia, integrate the system with other wellness devices and provide reminder notifications for users. The company is also expected to develop strategies for regulatory clearance and commercialization of the technology.
“I don’t want other people to go through what I went through.”
Emagine Solutions Technology is a six year-old company co-founded by Courtney Williams, now the company’s CEO. Williams revealed her own encounter with preeclampsia in an interview earlier this month with Authority Magazine, published on Medium.
I had a high risk pregnancy during the height of the Covid pandemic and I got preeclampsia in the postpartum period. I was frustrated by the lack of technology available to communicate my condition with my provider. Furthermore, if I had had this technology I would have known when my blood pressure was too high and when to seek help from my provider. … I was frustrated that I had to keep going into the office multiple times per week just to get my blood pressure read. I developed this technology because I don’t want other people to go through what I went through.
Also in the interview, Williams says her team interviewed more than 100 women during the height of the Covid-19 pandemic about their prenatal experiences showing extra burdens faced by Black, indigenous, and rural women. Respondents told about women lacking access to adequate insurance, being out-of-range from high-speed Internet or cellular networks supporting telemedicine, located in counties without an OB-GYN specialist, or feeling their needs were not being addressed by health care providers.
“The U.S. maternal health crisis is felt by every community in our country,” says Williams in a company statement released through BusinessWire. “The National Science Foundation provides vital funding, policy, and support that allows us to develop much-needed solutions, capture the attention of the nation, and drive real change.”
The NSF award is made through the agency’s Small Business Innovation Research or SBIR program. NSF says its program awards more than $200 million a year to some 400 start-ups in the U.S.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on July 22nd, 2023 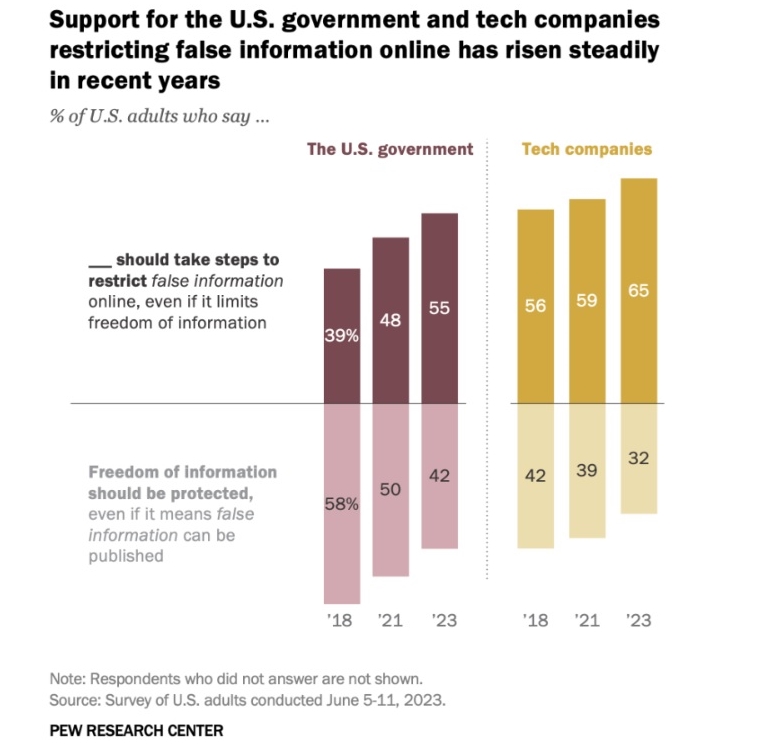 Click on image for full-size view (Pew Research Center) 22 July 2023. A recent survey shows majorities of American adults would like technology companies or the government to restrict the spread of false information online. Findings from the poll conducted in June 2023 were released this week by the Pew Research Center, the day before a White House meeting with tech industry executives on building safeguards into artificial intelligence systems.
The Pew Research survey asked its sample about actions needed to curb harmful online material, both false information and extremely violent content. Nearly two-thirds of Americans (65%) favor tech companies limiting false content online, with somewhat fewer, but still a majority (55%) wanting the government to step in and restrict false online content. Since Pew began asking this question, the share of Americans wanting the industry or government to restrict false online content has grown each time from 56 percent for tech companies and 39 percent for government action in 2018 to majorities of Americans today. Even larger percentages of Americans want limits on extremely violent content imposed by tech companies (71%) or government (60%).
As with many policy questions today, Republicans and Democrats differ on the government’s role in limiting false information online. About four in 10 Republicans (39%) would like to see the government curb false online content, while about six in 10 (59%) are opposed. Among Democrats, however, seven in 10 (70%) want government to restrict false information online, with roughly three in 10 (28%) are opposed. Moreover, the share of Democrats favoring government limits on false online content has grown from 40 percent in 2018, while the proportion of Republicans has barely changed from 37% that year.
Pew Research Center conducted the survey online with 5,115 U.S. adults taking part in the Center’s American Trends Panel from 5 to 11 June 2023. Participants are recruited through national random sampling of U.S. households, with results weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on July 21st, 2023  (A. Kotok) 21 July 2023. A biotechnology company designing immunotherapies for solid tumor cancers with a patient’s white blood cells is raising $80 million in its initial public offering or IPO. Turnstone Biologics Corp., an eight year-old enterprise in San Diego, trades its shares on the Nasdaq exchange under the symbol TSBX.
Turnstone Bio is a developer of solid tumor cancer treatments that it says makes up for shortcomings in conventional immunotherapies, notably for some patients with limited numbers of T-cell lymphocytes, white blood cells in the immune system, that recognize and attack tumors. The company says its technology screens and identifies a T-cell lymphocytes from a patient’s tumor that attack cancer cells after penetrating the tumor’s protective microenvironment.
Turnstone says it then isolates and expands the number of potent, targeted tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes or TILs in the lab, removing less effective T-cells to boost their potency, and re-infuses the cells back into the patient. An enhancement in that process, now in preclinical stages says the company, pre-treats tumors with engineered viruses that disrupt tumor cells and improve the collection of tumor-attacking T-cells. Following re-infusion of TILs, says Turnstone, engineered viruses reprogram the tumor microenvironment, and provide an easier target for TILs to attack cancer cells.
In early-stage clinical trials
In Oct. 2022, Turnstone Bio’s lead product code-named Tidal-1 received FDA clearance to begin early-stage clinical trials of TILs, testing the treatments in patients with breast and colorectal cancer, and uveal melanoma, a rare cancer affecting the dark pigment in eyes. A separate early-stage trial is underway with Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Florida in patients with cutaneous melanoma, the more common form of aggressive skin cancer, and melanoma occurring in other organs.
Turnstone Biologics was first formed in 2015, spun-off from cancer research labs at universities in Canada. As reported by Science & Enterprise in Dec. 2019, Turnstone Bio licensed its previous cancer immunotherapy technology to Takeda Pharmaceuticals in Japan. In Jan. 2021, the company acquired Myst Therapeutics and its TIL technology that now makes up Turnstone’s pipeline. According to Crunchbase, the company raised $132.7 million in four venture rounds since its founding.
For its IPO, Turnstone Bio issued some 6.7 million shares on the Nasdaq, priced at $12.00, but opening this morning at $11.40. At the closing bell today, the company’s shares were at $11.00, a decline of 8.3 percent from the IPO price.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on July 20th, 2023 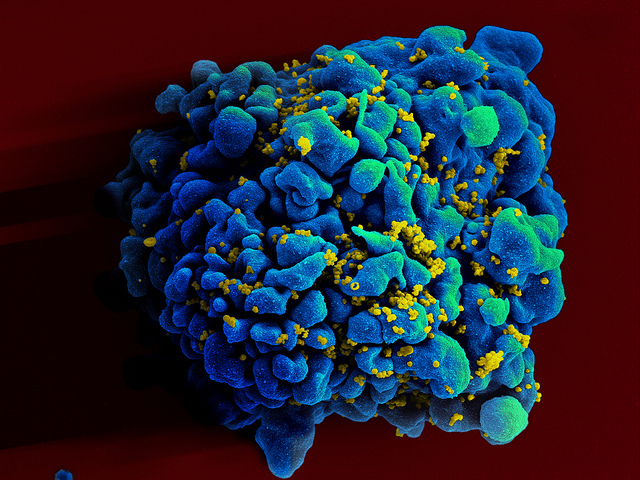 T-cell infected by HIV (NIAID, Flickr) 20 July 2023. A treatment for HIV taken just once, using the genome-editing technology Crispr, is receiving fast-track designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Excision BioTherapeutics Inc. in San Francisco, developer of the therapy code-named EBT-101, calls the one-time infusion a functional cure for HIV infections.
Human immunodeficiency virus or HIV attacks CD4 lymphocytes, white blood cells in the immune system, which weakens the body’s ability to prevent opportunistic and severe infections, such as tuberculosis. In advanced stages, people with HIV can contract acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or AIDS, a deadly condition. HIV is spread by exchange of bodily fluids, such as blood and semen, as well as from mother to child in pregnancy. According to World Health Organization, some 39 million people in the world are living with HIV, of which 25.6 million are in Africa. WHO estimates 630,000 people died from HIV-related infections in 2022, with 1.3 million new HIV cases that year.
The recommended care for HIV is antiretroviral therapy that suppresses the viral load, reducing risks of infection and spreading the disease to others. The treatments, taken daily in most cases, make it possible to renew CD4 white blood cells and reduce HIV to virtually undetectable levels. Yet HIV remains latent in people with HIV, who must continue taking antiretroviral treatments as prescribed during their lifetimes for the therapy to be effective.
Excision BioTherapeutics is an eight year-old company commercializing discoveries licensed from the labs of Crispr pioneer Jennifer Doudna at University of California in Berkeley — awarded the 2020 Nobel Prize in chemistry with Emmanuelle Charpentier for their discoveries of genome editing with Crispr — and HIV/AIDS researcher Kamel Khalili at Temple University. Crispr, short for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats, uses a technique based on bacterial defense mechanisms that harness RNA to identify, monitor, and edit specific locations in DNA.
Testing treatment at three dosage levels
EBT-101 is the company’s lead product, delivering its Crispr payload in a single intravenous infusion with a benign adeno-associated virus containing dual RNA guides. Those RNA guides send Cas9 editing enzymes to three sites in the HIV genome, where the edits remove large sections of DNA, preventing viral escape and reproduction. Excision Bio says EBT-101 disables HIV viruses, thus preventing further infections.
The company is testing EBT-101 in an early- and mid-stage clinical trial enrolling nine individuals with HIV and taking antiretroviral therapy, at three locations in the U.S. The study team is assessing the safety of EBT-101 at three dosage levels, looking primarily for incidence and severity of adverse effects from the treatments for 48 weeks. Trial participants can also take part in a follow-up study with semi-annual check-ups for five years, then annual reviews for another 10 years. Science & Enterprise reported on the start of the trial in Jan. 2022.
Excision Bio says today that FDA assigned a fast-track designation to EBT-101. Fast track status, according to FDA, is given to therapies, vaccines, or diagnostics for serious medical conditions showing superior effectiveness, reduced adverse effects or toxicities, improved diagnostics where early detection improves outcomes, or addressing major public health needs. The designation provides developers with more frequent access to FDA on drug development and clinical trials, review of new drug or biologic license applications in sections rather than waiting until all pass are complete, and eligibility for further accelerated reviews.
In a company statement released through Globe Newswire, Excision BioTherapeutics CEO Daniel Dornbusch notes, “This designation underscores the importance of finding a cure for people living with HIV and bolsters Excision’s efforts to rapidly develop potentially curative therapies for significant unmet medical needs.”
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
By Alan, on July 19th, 2023  Pentagon in Washington, D.C., headquarters of the U.S. Department of Defense (Army.mil) 19 July 2023. A synthetic biology company is receiving a contract with the U.S. advanced defense research agency to devise a high-speed localized process for making therapeutic proteins. Ginkgo Bioworks in Boston is receiving an $18 million award from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency or Darpa for a four-year project to develop the process.
The project is part of a Darpa initiative called reimagining protein manufacturing. Darpa says producing proteins at scale for medical countermeasures and therapeutics today requires a massive centralized infrastructure, complex pipelines, and long lead times for cellular engineering. As a result, says the agency, several months are needed for production alone, with more time needed to get protein-based therapies into the hands of front-line clinicians.
Darpa’s R&D process seeks transformational change instead of incremental advances when confronting a problem, often by collaboration with industry and academic partners, and providing encouragement and resources to focus on novel solutions. In this case, Darpa is seeking a process to manufacture medical-grade proteins that can respond within 24 hours when provided with a DNA or RNA target template, produce fully active and validly designed complex proteins, and in sufficient quantities to achieve their medical countermeasure mission. In addition, the process needs to work in “denied, degraded, or disrupted operational environments” often encountered by U.S. armed forces.
Based on cell-free protein synthesis
For this initiative, Ginkgo Bioworks is leading a team with partners from synthetic biology labs at Imperial College London and the biotechnology company Nature’s Toolbox Inc. in Rio Rancho, New Mexico. The team is tasked with devising techniques that adapt cell-free protein synthesis. This process employs transcription and translation mechanisms of living cells, but accelerates that process by separating the protein synthesis machinery from cells. Those mechanisms are then harnessed to produce complex proteins on demand, meeting specified design and functional properties.
Ginkgo Bioworks says it’s applying its foundry technology with computational biology and automation for design of synthetic DNA and organisms meeting functional specifications. The company says its codebase, a library of cells, enzymes, and genetic codes, provides templates for a head-start on new protein design, including more than 2 billion genes in some 8 million natural product gene clusters for synthetic proteins.
Ginkgo Bioworks says it plans to adapt its work for Darpa to devise a process that also meets commercial pharmaceutical production standards called Good Manufacturing Practices to encourage adoption by the pharmaceutical industry. “There is growing recognition that pharmaceutical supply chains are at risk,” says Ginkgo Bio co-founder and CEO Jason Kelly in a company statement. “One way to meet this challenge is distributed manufacturing at the point of care,” adding, “Imagine a future where drugs, including complex biologics, are produced locally or in a widely distributed manner on-demand.”
In Apr. 2023, Science & Enterprise reported on a similar undertaking by Ginkgo Bioworks, a collaboration with companies in the U.K. and Slovakia to advance a process for reducing the cost and increasing the scale of messenger ribonucleic acid or mRNA manufacturing. In synthetic forms, mRNA is used in vaccines and therapies to invoke specific immune responses, gaining recent popular recognition for Covid-19 vaccines.
More from Science & Enterprise:
We designed Science & Enterprise for busy readers including investors, researchers, entrepreneurs, and students. Except for a narrow cookies and privacy strip for first-time visitors, we have no pop-ups blocking the entire page, nor distracting animated GIF graphics. If you want to subscribe for daily email alerts, you can do that here, or find the link in the upper left-hand corner of the desktop page. The site is free, with no paywall. But, of course, donations are gratefully accepted.
* * *
|
Welcome to Science & Enterprise Science and Enterprise is an online news service begun in 2010, created for researchers and business people interested in taking scientific knowledge to the marketplace.
On the site’s posts published six days a week, you find research discoveries destined to become new products and services, as well as news about finance, intellectual property, regulations, and employment.
|











 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts
You must be logged in to post a comment.